hOORAY4@ngles!
GEOMETRY
The circumference of a circle is 2 * π * r
The diameter of a circle is 2 * r
The area of a circle is 2 * π * r²
C = 2πr
D = 2r
A = πr²
Rectangular shape
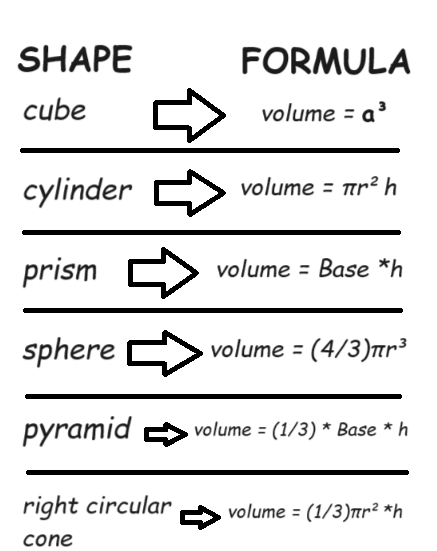
volume = length * width * height
Points, Lines, and Planes:
-
A point is a location in space.
-
A line is a straight path that extends infinitely in both directions.
-
A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
NEED TO KNOW

Angles:
-
An angle is formed by two rays with a common endpoint (vertex).
-
Types of angles include:
-
Acute Angle: Less than 90 degrees.
-
Right Angle: Exactly 90 degrees.
-
Obtuse Angle: More than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
-
Straight Angle: Exactly 180 degrees.
-
Reflex Angle: More than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
-

Triangles:
-
A triangle is a polygon with three sides.
-
Types of triangles include:
-
Equilateral: All sides are of equal length.
-
Isosceles: Two sides are of equal length.
-
Scalene: No sides are of equal length.
-
Right Triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
-

Quadrilaterals:
-
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides.
-
Types of quadrilaterals include:
-
Square: All sides are of equal length and angles are right angles.
-
Rectangle: Opposite sides are of equal length and angles are right angles.
-
Rhombus: All sides are of equal length.
-
Parallelogram: Opposite sides are parallel and equal in length.
-

Circles:
-
A circle is a set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point called the center.
-
Key terms:
-
Radius: Distance from the center to any point on the circle.
-
Diameter: Twice the radius.
-
Circumference: The perimeter of a circle (2 * π * radius).
-
Area: π * radius².
-
Area and Perimeter:
-
Area is the measure of the space inside a shape.
-
Perimeter is the total length of the sides of a shape.
-
Formulas for common shapes:
-
Rectangle:
-
Area = length * width
-
Perimeter = 2 * (length + width)
-
-
Triangle:
-
Area = (base * height) / 2
-
-
Circle:
-
Area = π * radius²
-
Circumference = 2 * π * radius
-
-

Volume:
-
Volume is the amount of space enclosed by a 3D shape
-
Formulas for common solids:
-
Cube: Volume = side³
-
Cylinder: Volume = π * radius² * height
-
Sphere: Volume = (4/3) * π * radius³
-

Transformations:
-
Translation: Sliding a shape without changing its size or shape.
-
Rotation: Turning a shape around a fixed point.
-
Reflection: Flipping a shape over a line.
Similarity and Congruence:
-
Similar Figures: Have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
-
Congruent Figures: Have the same shape and the same size.
Coordinate Geometry:
-
Coordinate Plane: A grid formed by an x-axis and a y-axis.
-
Distance Formula: Used to find the distance between two points.
-
Slope Formula: Used to find the slope of a line.